Home Study Continuing Pharmacy Education
Take advantage of remote CE learning. The Continuing Education Office provides up to date educational content from the University of Colorado anytime through our online learning platforms. We offer a variety of ACPE-accredited home study activities, some free, some requiring a fee - that you can complete from the comfort of your home.
Gender Affirming Care: Basics to Providing Care
This course is designed for healthcare professionals across various settings—including retail, inpatient, and outpatient clinics—who wish to enhance their understanding and skills in providing gender affirming care. With a focus on hormone therapies and other gender-affirming medications, often used off-label, this training will cover the recommended practices outlined in multiple healthcare guidelines. Participants will learn about the unique approaches to therapeutic targets and goals specific to gender affirming treatments.Managing Medications During Ramadan
The Skaggs School of Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Sciences is committed to fostering a diverse, equitable, and inclusive community. This three-part series will focus on Muslim patients and what healthcare providers need to consider when it comes to fasting practices during the holy month of Ramadan.

Medical Cannabis for Health Care Providers
Medical cannabis is legalized in 36 states, the District of Columbia and four U.S. territories. Twelve other states have laws that limit tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) content, for the purpose of allowing access to products that are rich in cannabidiol (CBD), another component of cannabis. While recreational cannabis is legalized in 18 states, the focus on the modules is on medical cannabis efficacy and safety.
Integrative Health and Natural Wellness
Integrative health has a rich global history and plays a crucial role in complementing traditional Western Medicine today. Pharmacists, as front-line healthcare providers, often face inquiries about the safety, efficacy, and usage of herbal supplements. This three-part series aims to help busy professionals identify reliable sources of dietary supplement information, and herbal remedies offering appropriate cautions for drug-supplement interactions and considerations for special or vulnerable populations.

Motivational Interviewing with Patient Scenarios
Motivational interviewing (MI) is essential for pharmacists as it enhances medication adherence, improves patient health outcomes, and fosters a trusting patient-provider relationship. By using MI, pharmacists can effectively explore patients' concerns and motivations, addressing issues such as fear of side effects, cost barriers, and lifestyle challenges in a compassionate, patient-centered manner.

OpenEvidence: A Sledgehammer in the AI Toolbox?
Artificial intelligence–enabled tools are rapidly becoming integrated into the medical literature and clinical decision-making landscape. As these technologies continue to evolve, pharmacists play a critical role in assessing the reliability, validity, and appropriate use of AI-generated information before applying it in patient care or professional collaboration.
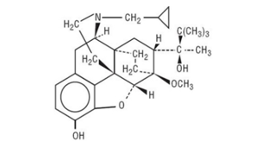
2022 CDC Clinical Practice Guideline for Prescribing Opioids: Deep Dive
This free educational program is open to physicians, advanced practice providers, nurses, and pharmacists. It provided an in-depth understanding of the 2022 Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) Clinical Practice Guideline for Prescribing Opioids for Pain and how to apply its recommendations in clinical practice.
.jpeg?sfvrsn=845fa6b4_0)
Chronic Pain Centers of Excellence Educational Series Best Practices in Managing Chronic Pain
This 2-hour educational program provides physicians, advance practice providers, and pharmacists with an understanding of best practices in chronic pain management and safe opioid prescribing in the primary care setting. Knowledge gained from this program will enhance a participant’s confidence in managing chronic pain in clinical practice and selecting the most appropriate therapeutic interventions.


